Ohms Law Calculator
Please provide any 2 values and click "Calculate" to get the other values in the ohm's law equations V = I × R and P = V × I.
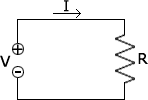 |
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage. This is true for many materials, over a wide range of voltages and currents, and the resistance and conductance of electronic components made from these materials remain constant. Ohm's Law is true for circuits that contain only resistive elements (no capacitors or inductors), regardless of whether the driving voltage or current is constant (DC) or time-varying (AC). It can be expressed using a number of equations, usually all three together, as shown below.
| V = I × R | ||||
| R = |
| |||
| I = |
| |||
Where:
R is resistance in Ohms
I is current in Amperes
Electrical Power
Power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit per unit time typically expressed in the SI (International System of Units) unit of Watts. Power is typically produced by electric generators and supplied to businesses and homes through the electric power industry, but can also be supplied by electric batteries or other sources.
In resistive circuits, Joule's Law can be combined with Ohm's Law to produce alternative expressions for the amount of power dissipated, as shown below.
| P = V × I | ||||
| P = |
| |||
| P = I2 × R | ||||
Where:
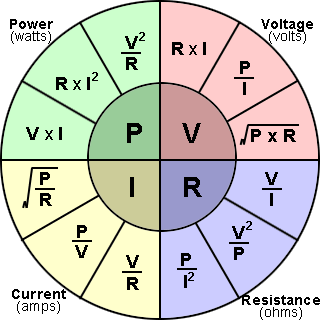
Ohm's Law Formula Wheel
Below is a formula wheel for Ohm's Law relationships between P, I, V, and R. This is essentially what the calculator does, and is just a representation of the algebraic manipulation of the equations above. To use the wheel, choose the variable to solve for in the middle of the wheel, then use the relationship for the two known variables within the cross section of the circle.